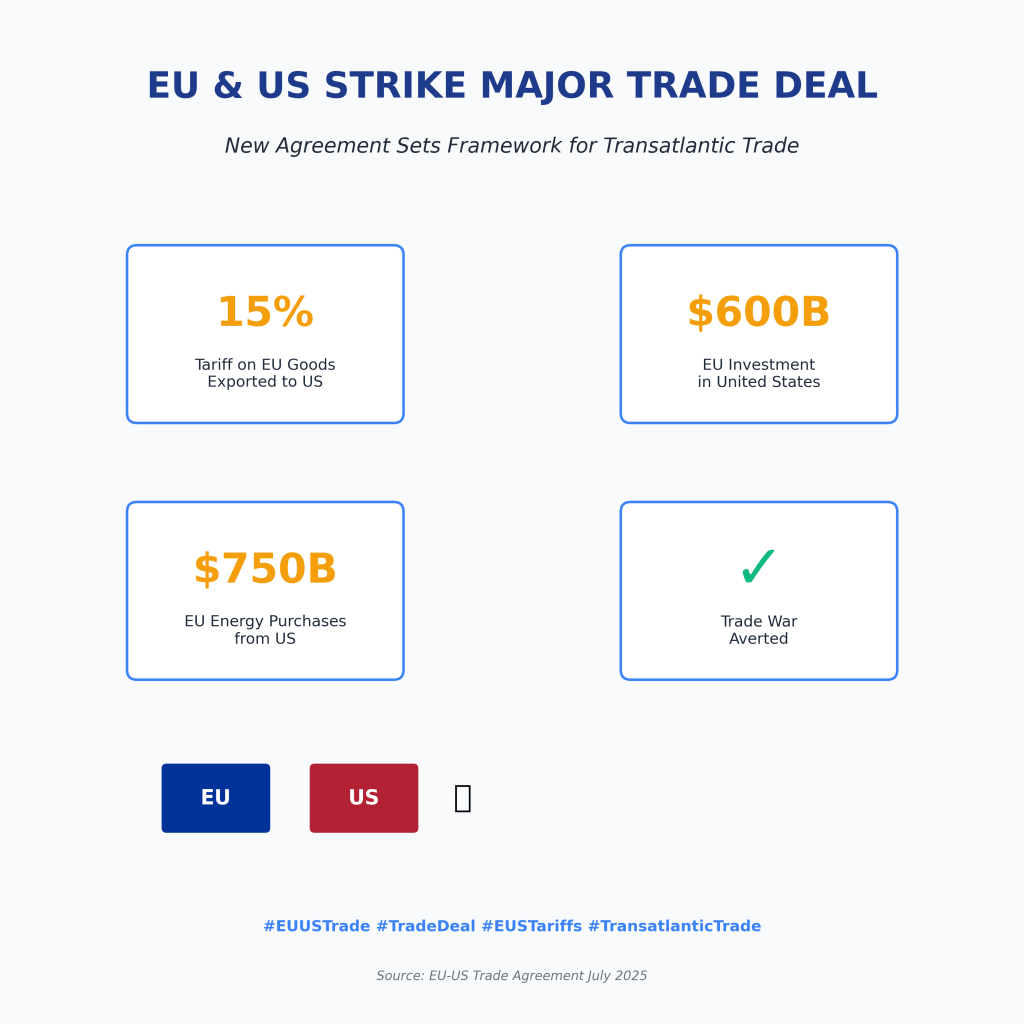
The new Trump-EU tariffs deal sets a 15% tariff on most EU exports to the US, with some strategic exemptions. For Spain, this means higher costs for key export sectors like automotive, olive oil, and pharmaceuticals, but also new opportunities to adapt and compete.
Introduction
The recent agreement between President Trump and the European Union has reshaped the landscape for transatlantic trade. With a 15% tariff now applied to most EU goods entering the US, Spanish exporters face both challenges and opportunities. Here’s a clear, structured look at what’s known so far, the economic implications for the EU and Spain, which Spanish products are most affected, and what steps can be taken to keep Spanish exports flowing.
Background: The New Tariffs Deal
- Date of Agreement: July 27, 2025
- Key Terms:
- 15% tariff on most EU exports to the US (down from a threatened 30%)
- Some products exempted under a «zero-for-zero» scheme (aircraft, certain chemicals, semiconductor equipment, some agricultural goods)
- EU to increase US energy purchases and investment
Economic Implications for the EU
The Big Picture
- Tariff Increase: From an average of 1.2% to 15% on most goods
- GDP Impact: Estimated contraction of 0.3% for the EU, with export volumes to the US expected to drop by 0.6% to 1.1%
- Most Affected Sectors:
- Automotive
- Pharmaceuticals
- Machinery and electronics
- Steel and aluminum (still at 50% tariff)
- Exemptions: Aircraft, some chemicals, semiconductor equipment, and select agricultural products
Key Aspect:
The deal avoids a full-scale trade war, but EU exporters will face higher costs and reduced competitiveness in the US market.
Focus on Spain: Impact and Product Lines
Spanish Exports to the US: The Numbers
- Share of Total Exports: 4.7%
- Share of GDP: 1.1%
- Total Value (2025): $5,825 million
- Exports Now Facing Higher Tariffs: 95.3% (approx. $5,550 million)
- Total Additional Annual Cost: $875 million
Main Product Lines Affected
| Product Category | Export Value (M USD) | New Tariff | Additional Cost (M USD) | Impact Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | 1,200 | 15% | 166 | High |
| Olive Oil | 420 | 15% | 58 | Medium |
| Pharmaceuticals | 850 | 15% | 117 | High |
| Machinery & Equipment | 950 | 15% | 131 | High |
| Steel & Aluminum | 320 | 50% | 156 | Severe |
| Wine | 180 | 15% | 25 | Low |
| Chemicals | 680 | 15% | 94 | Medium |
| Petroleum Oils | 550 | 15% | 76 | Medium |
Product Lines Exempted or Less Affected
| Product Category | Export Value (M USD) | Tariff Status |
|---|---|---|
| Aircraft & Components | 190 | Exempt |
| Semiconductor Equipment | 85 | Exempt |
| Certain Chemicals | (part of 680) | Exempt (pending details) |
| Some Agricultural Goods | (part of 240) | Exempt (pending details) |
Analysis: What Does This Mean for Spain?
- Automotive, pharmaceuticals, and machinery are the hardest hit, with significant additional costs and potential loss of market share.
- Olive oil and wine—flagship Spanish agri-food exports—face new headwinds, though strong US demand may cushion the blow for bulk shipments.
- Steel and aluminum remain under severe pressure due to the unchanged 50% tariff.
- Aircraft, semiconductor equipment, and some chemicals are currently shielded, offering a lifeline for those sectors.
Key Aspect:
The vast majority of Spanish exports to the US are now less competitive, but a handful of strategic sectors remain protected.
Recommendations: How Spain Can Respond
- Diversify Export Destinations
- Continue expanding into ASEAN, Latin America, and Oceania to reduce reliance on the US market.
- Adapt Value Chains
- For agri-food (e.g., olive oil), consider investing in US-based bottling or packaging to bypass tariffs on finished goods.
- Leverage Exemptions
- Focus on growing exports in exempted categories (aircraft, semiconductors, certain chemicals, and agricultural products as details emerge).
- Monitor Ongoing Negotiations
- Stay alert for updates, as more products may be added to the exempted list in the coming weeks.
- Government Support
- Tap into available support programs, such as the €14.32 billion plan for agri-food exporters, to offset tariff impacts.
- Enhance Product Value
- Invest in branding, quality, and innovation to justify higher prices and maintain US market share despite tariffs.
Conclusion
The Trump-EU tariffs deal brings stability but at a cost: higher tariffs on most Spanish exports to the US. While some sectors are protected, the majority will need to adapt quickly—by diversifying markets, optimizing value chains, and focusing on exempted products. The situation remains fluid, and Spanish exporters should stay proactive to turn these challenges into new opportunities.
Summary Box:
- 15% tariff on most Spanish exports to the US
- Key sectors hit: automotive, olive oil, pharmaceuticals
- Aircraft, semiconductors, and some chemicals are exempt
- Strategic adaptation and diversification are essential for continued growth